SMS:Functional Surfaces: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
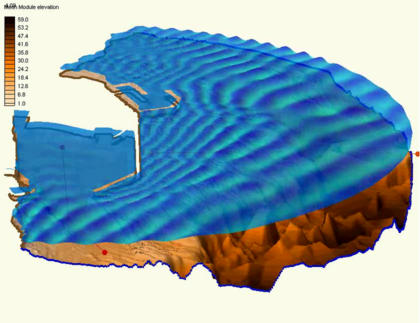
A functional surface is exactly that. It is a surface representing one of the functional datasets associated with a mesh, grid or TIN. The most intuitive example of a functional surface is the display of the water surface over a model's bathymetry. In this case, the surface represents an actual physical surface, but the functional surface could just as easily represent the velocity magnitude, or concentration, or any other scalar quantity. | A functional surface is exactly that. It is a surface representing one of the functional datasets associated with a mesh, grid or TIN. The most intuitive example of a functional surface is the display of the water surface over a model's bathymetry. In this case, the surface represents an actual physical surface, but the functional surface could just as easily represent the velocity magnitude, or concentration, or any other scalar quantity. | ||
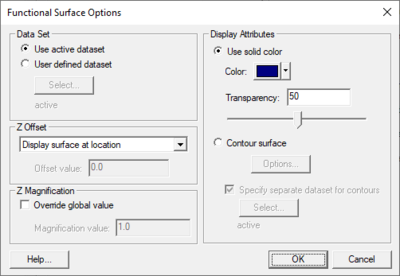
[[Image:SMS Functional Surface Opt. | [[Image:SMS Functional Surface Opt.png|thumb|400 px|''Functional Surfaces Options'' dialog]] | ||
To create/display functional surfaces, enable them in the display options of the appropriate module, and specify their attributes which include: | To create/display functional surfaces, enable them in the display options of the appropriate module, and specify their attributes which include: | ||
* ''Dataset'' – Selects which dataset is to be used to form the functional surface. | * ''Dataset'' – Selects which dataset is to be used to form the functional surface. | ||
:* Use active dataset | :* ''Use active dataset'' – The currently selected dataset will be used for the functional surface. | ||
:* User defined dataset | :* ''User defined dataset'' – Allows selecting a specific dataset in the project to use for the functional surface. The '''Select''' button for this option will bring a ''Select Dataset'' dialog. | ||
* ''Z Offset'' – SMS displays functional surfaces at a simulated z-value. This may be the actual surface value (such as is the case with water surfaces elevations), but more often the value will not have a physical meaning, and may intersect the bathymetry or not even be in the same area. For this reason, SMS offers options for placing the functional surface at | * ''Z Offset'' – SMS displays functional surfaces at a simulated z-value. This may be the actual surface value (such as is the case with water surfaces elevations), but more often the value will not have a physical meaning, and may intersect the bathymetry or not even be in the same area. For this reason, SMS offers options for placing the functional surface at one of the following locations: | ||
** "Display surface at location" – The functional surface will be displayed at the location of the dataset on the geometry. | |||
**"Display surface above geometry" – The functional surface will be displayed slightly above the geometry based on the z-magnification. | |||
**"Display surface with user defined offset" – The functional surface will be display based on a value entered by the user. | |||
***''Offset value'' – Enter an offset Z value for the user defined offset. | |||
* ''Z Magnification'' – Functional data may not vary significantly when compared to the horizontal extents of the model. For this reason, the interface allows magnification (scaling) of the functional surface. By default, the surface is scaled based on the global z-magnification specified in the general display options. This may be overridden. | * ''Z Magnification'' – Functional data may not vary significantly when compared to the horizontal extents of the model. For this reason, the interface allows magnification (scaling) of the functional surface. By default, the surface is scaled based on the global z-magnification specified in the general display options. This may be overridden. | ||
:* Override global value | :* ''Override global value'' – Turn on to override the global Z magnification value. | ||
:* Magnification value | :** ''Magnification value'' – Enter a z magnification value to override the global value. | ||
* ''Display Attributes'' – Controls the color of the functional surface. It may be a constant color or colored based on the contour colors specified. The colors may be associated with the value of the functional surface, or another dataset. The surface may also be partially transparent. | * ''Display Attributes'' – Controls the color of the functional surface. It may be a constant color or colored based on the contour colors specified. The colors may be associated with the value of the functional surface, or another dataset. The surface may also be partially transparent. | ||
:* Use solid color | :* ''Use solid color'' – Will change the functional surface to be a single color. | ||
:* Transparency | :**''Color'' – Select a color to use as the solid color for the functional surface. | ||
:* Contour surface | :* ''Transparency'' – Set a transparency level for the functional surface. The transparency by entering a value or using the slider. | ||
:* Specify separate dataset for contours | :* ''Contour surface'' – Sets specific contour options for the functional surface. | ||
:** '''Options''' – Will open the ''Dataset Contour Options'' dialog. | |||
:** ''Specify separate dataset for contours'' – Allows a different dataset to be used for the contour options. | |||
:*** '''Select''' – Brings up a ''Select Dataset'' dialog. | |||
Latest revision as of 23:12, 8 November 2022
At a glance
- Surface with elevation based upon scalar dataset values
- Very useful for wave models and models with large change in water surface elevation
- Elevations can be exaggerated to better visualize dataset variations
- Surfaces can have a solid color or use color filled contours
- Transparency can be used to allow see through surfaces
A functional surface is exactly that. It is a surface representing one of the functional datasets associated with a mesh, grid or TIN. The most intuitive example of a functional surface is the display of the water surface over a model's bathymetry. In this case, the surface represents an actual physical surface, but the functional surface could just as easily represent the velocity magnitude, or concentration, or any other scalar quantity.
To create/display functional surfaces, enable them in the display options of the appropriate module, and specify their attributes which include:
- Dataset – Selects which dataset is to be used to form the functional surface.
- Use active dataset – The currently selected dataset will be used for the functional surface.
- User defined dataset – Allows selecting a specific dataset in the project to use for the functional surface. The Select button for this option will bring a Select Dataset dialog.
- Z Offset – SMS displays functional surfaces at a simulated z-value. This may be the actual surface value (such as is the case with water surfaces elevations), but more often the value will not have a physical meaning, and may intersect the bathymetry or not even be in the same area. For this reason, SMS offers options for placing the functional surface at one of the following locations:
- "Display surface at location" – The functional surface will be displayed at the location of the dataset on the geometry.
- "Display surface above geometry" – The functional surface will be displayed slightly above the geometry based on the z-magnification.
- "Display surface with user defined offset" – The functional surface will be display based on a value entered by the user.
- Offset value – Enter an offset Z value for the user defined offset.
- Z Magnification – Functional data may not vary significantly when compared to the horizontal extents of the model. For this reason, the interface allows magnification (scaling) of the functional surface. By default, the surface is scaled based on the global z-magnification specified in the general display options. This may be overridden.
- Override global value – Turn on to override the global Z magnification value.
- Magnification value – Enter a z magnification value to override the global value.
- Override global value – Turn on to override the global Z magnification value.
- Display Attributes – Controls the color of the functional surface. It may be a constant color or colored based on the contour colors specified. The colors may be associated with the value of the functional surface, or another dataset. The surface may also be partially transparent.
- Use solid color – Will change the functional surface to be a single color.
- Color – Select a color to use as the solid color for the functional surface.
- Transparency – Set a transparency level for the functional surface. The transparency by entering a value or using the slider.
- Contour surface – Sets specific contour options for the functional surface.
- Options – Will open the Dataset Contour Options dialog.
- Specify separate dataset for contours – Allows a different dataset to be used for the contour options.
- Select – Brings up a Select Dataset dialog.
- Use solid color – Will change the functional surface to be a single color.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||