GMS:MF6 LAK Package: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
{{MF6 Time Series Files Dialog}} | {{MF6 Time Series Files Dialog}} | ||
{{MF6 Observation Files Dialog}} | {{MF6 Observation Files Dialog}} | ||
{{MF6 Add Stresses Dialog}} | |||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
Revision as of 20:40, 21 February 2020
| This contains information about functionality available starting at GMS version 10.5. The content may not apply to other versions. |
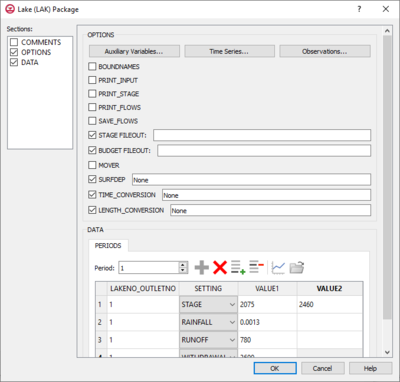
The Lake (LAK) Package dialog is accessed by double-clicking on the WEL package under a MODFLOW 6 simulation in the Project Explorer. It contains the following sections and options:
- Sections list – A list of sections that can be turned on or off:
- Comments – Turn on to make the Comments section visible.
- Options – Turn on to make the Options section visible.
- Data – Turn on to make the Data section visible. This section is on by default.
- Comments section – Enter general alphanumeric comments. Comments entered here get written at the top of the file, preceded by a '#' symbol.
- Options section – Temporal options and settings:
- Auxiliary Variables... – Click to bring up the Auxiliary Variables dialog.
- Time Series... – Click to bring up the Time Series Files dialog.
- Observations... – Click to bring up the Observation Files dialog.
- Options section – Temporal options and settings:
- BOUNDNAMES – If turned on, indicates that the list of lake cells will be provided with the associative boundary names.
- PRINT_INPUT – If turned on, indicates that the list of lake information will be written to the listing file after it is read.
- PRINT_STAGE – If turned on, indicates that lake stages will be printed to the listing file for each stress period if "HEAD PRINT" is specified.
- PRINT_FLOWS – If turned on, indicates that a list of lake flow rates will be printed to the listing file.
- SAVE_FLOWS – If turned on, indicates that the lake flow terms will be written to a specified file.
- STAGE_FILEOUT – Indicates that the record corresponds to a specific stage. Also allows the written indication of stage information.
- BUDGET_FILEOUT – Allows the specification of a file to which desired flow terms will be written.
- NO_WELL_STORAGE – If turned on, indicates that well storage will not be included in the continuity equation. It is used to control discharge rate oscillations.
- SURFDEP – When turned on, allows the a written value that defines the surface depression depth of the lake.
- MOVER – When turned on, indicates that the Lake (Lak) Package, in this instance can be used in collaboration with the Water Mover (MVR) Package.
- TIME_CONVERSION – Value that is used in converting outlet flow terms into time units.
- LENGTH_CONVERSION – Value that is used in converting outlet flow terms into length units.
- Data section – Contains the following:
- Periods drop-down – Use the Increment Up and Down
 buttons to select the desired period.
buttons to select the desired period. - Define Period
 – If no period is defined, click to make the spreadsheet editable.
– If no period is defined, click to make the spreadsheet editable. - Delete Period
 – Click to delete the existing period.
– Click to delete the existing period. - Add Rows
 – Click to bring up the Add Stresses dialog.
– Click to bring up the Add Stresses dialog. - Delete Rows
 – Click to bring up a dialog with three options:
– Click to bring up a dialog with three options:
- Delete from All Periods – Click to delete matching stresses from all periods.
- Delete from Just This Period – Click to delete matching stresses from just this period.
- Plot All Periods
 – Click to bring up the XY Series Editor dialog. Requires that a cell be selected in the table.
– Click to bring up the XY Series Editor dialog. Requires that a cell be selected in the table. - Open Time Series
 – Click to bring up the
– Click to bring up the - Filter on Selected Cells
 – Click to turn on filtering on the selected cells.
– Click to turn on filtering on the selected cells. - Table – Allows the manual input of different variables for the MAW Package.
- LAKENO_OUTLETNO – A value that defines the reach number associated with the specified PERIOD data.
- SETTING – Information that is linked to keywords and values.
- VALUE1 – Value to be entered in relation to the specific project.
- VALUE2 – Value to be entered in relation to the specific project.
- Periods drop-down – Use the Increment Up and Down
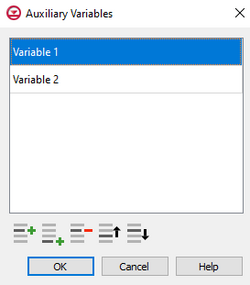
Auxiliary Variables Dialog
The Auxiliary Variables dialog is accessed by clicking Auxiliary Variables... in the Options section of many package dialogs. It is used to define an array of one or more auxiliary variable names. It contains the following sections and buttons:
- At the top is an unlabeled section listing all of the variables, one per line. Double-click on a variable name to rename it.
- Insert Row
 – Click to insert a row above the currently-selected row.
– Click to insert a row above the currently-selected row. - Add Row
 – Click to add a row below the currently-selected row.
– Click to add a row below the currently-selected row. - Delete Row
 – Click to delete the selected row.
– Click to delete the selected row. - Move Up
 – Move the selected row up.
– Move the selected row up. - Move Down
 – Move the selected row down.
– Move the selected row down.
Note that each variable name must be unique. If two or more variables share a name, variables added since opening the dialog will not be saved.
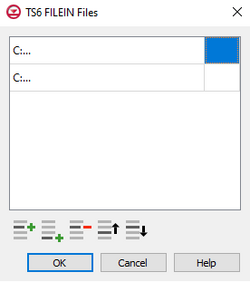
Time Series Files Dialog
The Time Series Files dialog is accessed by clicking Time Series Files... in the Options section of many of the package dialogs. It is used to define an array of one or more time series files. It contains the following sections and buttons:
- At the top is an unlabeled section listing all of the time series files, one per line.
- Double-click on the first field to see the full file path and name.
- Click Edit... to open the time series file.
- Insert Row
 – Click to insert a row above the currently-selected row.
– Click to insert a row above the currently-selected row. - Add Row
 – Click to add a row below the currently-selected row.
– Click to add a row below the currently-selected row. - Delete Row
 – Click to delete the selected row.
– Click to delete the selected row. - Move Up
 – Move the selected row up.
– Move the selected row up. - Move Down
 – Move the selected row down.
– Move the selected row down.
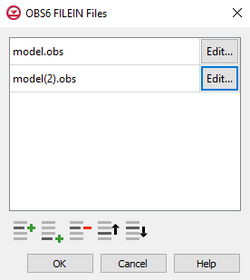
Observation Files Dialog
The Observation Files dialog is accessed by clicking Observations... in the Options section of many of the package dialogs. It is used to define an array of one or more observation files. It contains the following sections and buttons:
- At the top is an unlabeled section listing all of the observation files, one per line.
- Double-click on the first field to see the full file path and name.
- Click Edit... to open the Observations (OBS) Dialog.
- Insert Row
 – Click to insert a row above the currently-selected row.
– Click to insert a row above the currently-selected row. - Add Row
 – Click to add a row below the currently-selected row.
– Click to add a row below the currently-selected row. - Delete Row
 – Click to delete the selected row.
– Click to delete the selected row. - Move Up
 – Move the selected row up.
– Move the selected row up. - Move Down
 – Move the selected row down.
– Move the selected row down.
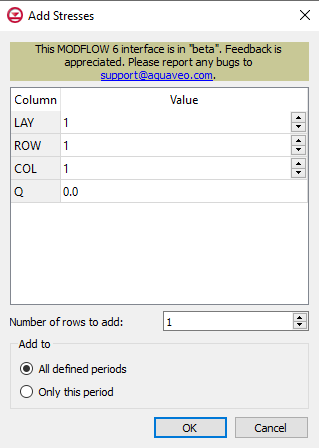
Add Stresses Dialog
The Add Stresses dialog is accessed by clicking Add Rows ![]() in the Periods section of several MODFLOW 6 package dialogs. It contains the following sections and options:
in the Periods section of several MODFLOW 6 package dialogs. It contains the following sections and options:
- Table – Table Options differ according to each package. See chart below.
- Number of rows to add – Use the Increment Up and Down
 buttons to select the desired number of rows to add.
buttons to select the desired number of rows to add.
- Add to section – Radio buttons with the following options:
- All defined periods – Select to add the rows to all defined periods.
- Only this period – Select to add the rows to only this period.
| Package | Add Stresses Dialog Table Options | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CHD |
| ||
| DRN |
| ||
| GHB |
| ||
| HFB |
| ||
| LAK |
| ||
| MAW |
| ||
| RIV |
| ||
| SFR |
| ||
| UZF |
| ||
| WEL |
|
Related Topics
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||