GMS:UGrid Interpolation: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
**''Use all time steps'' – If there are time steps, this option will interpolate all time steps in the source dataset. | **''Use all time steps'' – If there are time steps, this option will interpolate all time steps in the source dataset. | ||
*''Interpolating to'' – This data tree shows all objects that can receive the interpolated data. Select the object that will receive the new interpolated dataset. | *''Interpolating to'' – This data tree shows all objects that can receive the interpolated data. Select the object that will receive the new interpolated dataset. | ||
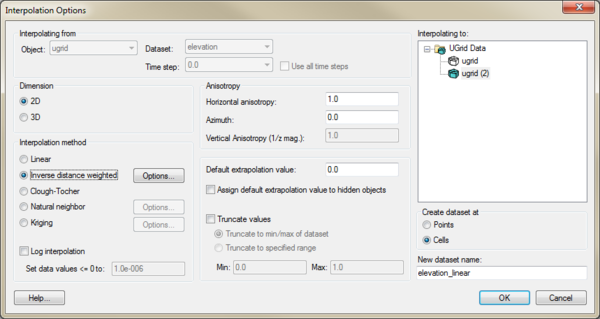
*''Dimension'' | *''Dimension'' – Options in this section determine whether the interpolation will be two-dimensional or three dimensional. | ||
**''2D'' | **''2D'' – Designates the interpolation as two-dimensional data. All interpolation methods are available with this option. | ||
**''3D'' | **''3D'' – Specified the interpolation as three-dimensional data. Only the inverse distance weighted and Kriging options are available with this method. | ||
*''Anisotropy'' | *''Anisotropy'' | ||
**''Horizontal anisotropy'' | **''Horizontal anisotropy'' | ||
**''Azimuth'' | **''Azimuth'' | ||
**''Vertical Anisotropy (1/z mag)'' | **''Vertical Anisotropy (1/z mag)'' | ||
*''Interpolation method'' | *''Interpolation method'' – This section specifies which interpolation process will be used. | ||
**''Linear'' | **[[GMS:Linear|''Linear'']] – Uses data points that are first triangulated to form a network of triangles. | ||
**''Inverse distance weighted'' | **[[GMS:Inverse Distance Weighted|''Inverse distance weighted'']] – Creates an interpolated surface that is a weighted average of the point data; the weight assigned to each point diminishes as the distance to the interpolation location increases. The '''Options''' button next to this option will bring up either the ''2D IDW Interpolation Options'' dialog or the ''3D IDW Interpolation Options'' dialog. | ||
**''Clough-Tocher'' | **[[GMS:Clough-Tocher|''Clough-Tocher'']] – A finite element method that has origins in the finite element method of numerical analysis. | ||
**''Natural neighbor'' | **[[GMS:Natural Neighbor|''Natural neighbor'']] – Based on the Thiessen polygon network of the point data. The '''Options''' button next to this option will bring up the ''Natural Neighbor Options'' dialog. | ||
**''Kriging'' | **[[GMS:Kriging|''Kriging'']] – Based on the assumption that the parameter being interpolated can be treated as a regionalized variable. The '''Options''' button next to this option will bring up the [[GMS:Kriging Options|''Kriging Options'']] dialog. | ||
**''Log interpolation'' | **''Log interpolation'' | ||
**''Set data value <=0 to'' | **''Set data value <=0 to'' | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
**''Points'' | **''Points'' | ||
**''Celss'' | **''Celss'' | ||
*''New dataset name'' | *''New dataset name'' – Assigns a name to the new dataset created from the interpolation process. | ||
It is also possible to drag a UGrid dataset and drop it on to another UGrid to open this dialog and indicate what the interpolation target is. | It is also possible to drag a UGrid dataset and drop it on to another UGrid to open this dialog and indicate what the interpolation target is. | ||