GMS:UGrid Inverse Distance Weighted Interpolation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*[[GMS:Quadratic Nodal Functions|Quadratic Nodal Functions]] – Makes use of quadratic polynomials to constrain nodal functions. | *[[GMS:Quadratic Nodal Functions|Quadratic Nodal Functions]] – Makes use of quadratic polynomials to constrain nodal functions. | ||
*[[GMS:Subset Definition|Subset Definition]] – Uses a subset of the data points in the computation of the nodal function coefficients and in the computation of the interpolation weights. | *[[GMS:Subset Definition|Subset Definition]] – Uses a subset of the data points in the computation of the nodal function coefficients and in the computation of the interpolation weights. | ||
*''Truncate values'' – This section allows for limiting the interpolated values to lie between the minimum and maximum value. | |||
**''Truncate to min/max of dataset'' – Limits the interpolated values to the minimum and maximum values in the original dataset. | |||
**''Truncate to specified range'' – Allows setting a user specified minimum and maximum value range. | |||
**''Min'' – Manually sets a minimum value. | |||
**''Max'' – Manually sets a maximum value. | |||
*'''Advanced''' – This button will open the ''Interpolate – Advanced'' dialog where options for anisotropy and extrapolation can be adjusted. | |||
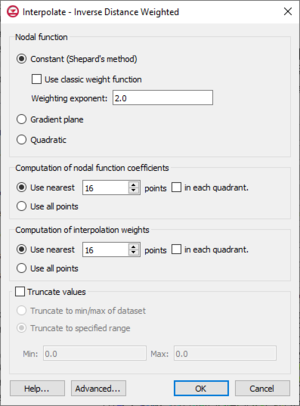
[[File:Interpolate-IDW.png|thumb|none|left|300 px|An example of the ''Interpolate – Inverse Distance Weighted'' dialog.]] | [[File:Interpolate-IDW.png|thumb|none|left|300 px|An example of the ''Interpolate – Inverse Distance Weighted'' dialog.]] | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 31 August 2018
One of the most commonly used techniques for interpolation of point data is inverse distance weighted (IDW) interpolation. Inverse distance weighted methods are based on the assumption that the interpolating surface should be influenced most by the nearby points and less by the more distant points. The interpolated surface is a weighted average of the point data; the weight assigned to each point diminishes as the distance to the interpolation location increases. Several options are available for inverse distance weighted interpolation. The options are selected using the IDW Interpolation Options dialog. This dialog is accessed through the Options button next to the Inverse distance weighted item in the Interpolate UGrid to UGrid dialog.
The options in the dialog are as follows:
- Constant Nodal Functions (Shepard's Method) – The simplest form of inverse distance weighted interpolation. Includes the option to use classic weight function by enter a weighting exponent.
- Gradient Plane Nodal Functions – Variation of Shepard's method with nodal functions or individual functions defined at each point
- Quadratic Nodal Functions – Makes use of quadratic polynomials to constrain nodal functions.
- Subset Definition – Uses a subset of the data points in the computation of the nodal function coefficients and in the computation of the interpolation weights.
- Truncate values – This section allows for limiting the interpolated values to lie between the minimum and maximum value.
- Truncate to min/max of dataset – Limits the interpolated values to the minimum and maximum values in the original dataset.
- Truncate to specified range – Allows setting a user specified minimum and maximum value range.
- Min – Manually sets a minimum value.
- Max – Manually sets a maximum value.
- Advanced – This button will open the Interpolate – Advanced dialog where options for anisotropy and extrapolation can be adjusted.
Related Topics
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||