WMS:Colorado State Lag Time Equation: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
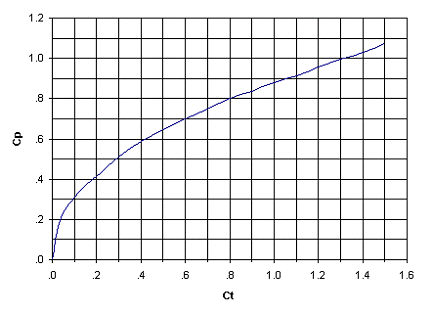
An equation used to compute lag time for watersheds in the Denver Colorado area was developed at Colorado State University. This equation was primarily used for watersheds in which there was some amount of developed land. It is not valid for watersheds with less than 10 percent impervious area ( | An equation used to compute lag time for watersheds in the Denver Colorado area was developed at Colorado State University. This equation was primarily used for watersheds in which there was some amount of developed land. It is not valid for watersheds with less than 10 percent impervious area (I<sub>a</sub>). The equation uses a runoff coefficient which represents variations in topography. This coefficient can also be used to compute the peaking factor using the relationship shown in the chart below. | ||
:<math>C_t = \frac {7.81}{I_a ^{0.78}}</math> | :<math>C_t = \frac {7.81}{I_a ^{0.78}}</math> | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
where: | where: | ||
< | :''C<sub>t</sub>'' = coefficient of watershed topography based on impervious area. | ||
< | :''I<sub>a</sub>'' = percentage of impervious area in the watershed (must be defined in the HEC-1 Loss methods). | ||
< | :''T<sub>LAG</sub>'' = watershed lag time in hours. | ||
:''L'' = maximum flow path length in miles. | |||
< | :''L<sub>ca</sub> = length to the centroid in miles. | ||
[[Image:PeakCoefficientGraph.jpg|frame|none|Graph for Determining the Peaking Coefficient | [[Image:PeakCoefficientGraph.jpg|frame|none|Graph for Determining the Peaking Coefficient C<sub>p</sub> from C<sub>t</sub>.]] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{WMSMain}} | {{WMSMain}} | ||
[[Category:Equations| | [[Category:Equations|Colorado]] | ||
[[Category:WMS Basins|Colorado]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:11, 29 September 2017
An equation used to compute lag time for watersheds in the Denver Colorado area was developed at Colorado State University. This equation was primarily used for watersheds in which there was some amount of developed land. It is not valid for watersheds with less than 10 percent impervious area (Ia). The equation uses a runoff coefficient which represents variations in topography. This coefficient can also be used to compute the peaking factor using the relationship shown in the chart below.
where:
- Ct = coefficient of watershed topography based on impervious area.
- Ia = percentage of impervious area in the watershed (must be defined in the HEC-1 Loss methods).
- TLAG = watershed lag time in hours.
- L = maximum flow path length in miles.
- Lca = length to the centroid in miles.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||