WMS:HEC-RAS
HEC-RAS is a one-dimensional model for computing water surface profiles for steady state or gradually varied flow. HEC-RAS supports networks of channels and is capable of modeling subcritical, supercritical, and mixed flow regime profiles. HEC-RAS is able to model obstructions in the flow path.
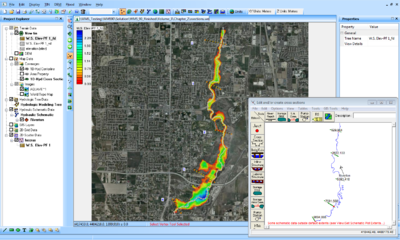
The WMS interface to HEC-RAS includes tools for setting up the river networks and cross sections as well as post-processing capabilities. WMS reads and writes the HEC-GeoRAS GIS import format. The HEC-RAS model is included with all paid editions of WMS (10.1 comes with HEC-RAS 5.0.1).
The first step to using HEC-RAS with WMS is to set up the river schematic. For information on the tools and processes to set up a river schematic, see the 1D River Hydraulic Module. Specific attributes for an HEC-RAS simulation include:
Assigning Materials
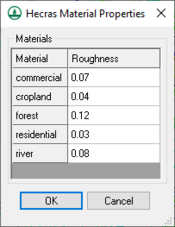
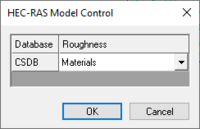
Roughness values for HEC-RAS are tied to materials in WMS which must be assigned as line properties inside the cross-section database. To assign roughness values to the materials, choose HEC-RAS | Material Properties. Also, the property type that is being used for the material values must be specified in the model control dialog. This dialog is accessed by selecting HEC-RAS | Model Control from the menu.
Running HEC-RAS
Before loading the data into HEC-RAS, the simulation needs to be saved in HEC-RAS GIS export format. This is done by using File | Save As and changing the type to HEC-RAS GIS export format. The file can then be loaded into HEC-RAS by choosing HEC-RAS | Import GIS File inside the geometry editor. See HEC-RAS documentation for information about setting up boundary conditions and running the model.
Once the solution has been generated the data may be used in WMS for post-processing. The data must first be exported to GIS format from within HEC-RAS (Under the HEC-RAS menu choose Export GIS File). This file can be opened inside of WMS. Once this solution data has been loaded into WMS, plots can be generated from the solution. For information on how to use the post-processing tools that are found in WMS, see the 1D hydraulic Module document.
HEC-RAS Menu
The HEC-RAS interface in WMS includes the HEC-RAS menu in the Hydraulic module. The menu has the following commands:
- Import GIS File – Loads GIS files into the HEC-RAS model instead of the GIS module.
- Export GIS File – Exports the solution data into GIS project file format for use in post-processing. Launches the HEC-RAS program.
- Read Floodplain Boundary – Loads a HEC-RAS GIS file (*.sdf) containing a floodplain boundaries.
- Set Project Filename – Opens GIS project file into HEC-RAS.
- Load Project – Allows defining the current working HEC-RAS project and will prompt for the filename of an existing HEC-RAS project. While the WMS interface does not allow developing a complete HEC-RAS model, it is possible to launch the HEC-RAS compute engine, or the GUI, by having a project handle in WMS. The Load Project command allows defining the current working HEC-RAS project and will prompt for the filename of an existing HEC-RAS project.
- Start – Launches the HEC-RAS software. WMS allows model linkages between HEC-1, HEC-RAS, and floodplain delineation for the purpose of performing stochastic simulation. These simulations can be developed from either of the three modeling menus. Read more about the stochastic simulation in the Stochastic Modeling article.
- Run Simulation – Allows starting an HEC-RAS project from within WMS. WMS does not provide a complete GUI to HEC-RAS and so the HEC-RAS interface itself must be used to finish model development. However, once the model has been completed it can be run from within WMS (this is primarily to facilitate flood plain delineation and stochastic simulations) by specifying the project name.
- Read Solution – Reads the water surface elevation for each cross section after an HEC-RAS model run. A scatter point set is created with a scatter point at the intersection of each cross section and the centerline. The Interpolate Results command in the River Tools menu of the Map module can be used to create a more dense set of scatter points that are more suitable for floodplain delineation.
- Plot Solution – Allows sending a solution to the HEC-RAS user interface for plotting.
- Delete Simulation – Removes the link WMS maintains to the current HEC-RAS simulation project file.
- Materials – Opens the Materials Data dialog.
- Material Properties – Brings up the HEC-RAS Material Properties dialog for assigning roughness values to the materials.
- Model Control – Brings up the HEC-RAS Model Control dialog.
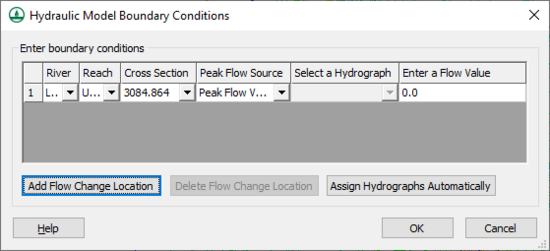
- Hydraulic Model Flow BC – Opens the Hydraulic Model Boundary Conditions dialog.
- Set Hydraulic Model Flow BC – Brings up the Hydraulic Model Boundary Conditions dialog for setting model flow.
- Stochastic Modeling – Brings up the Stochastic Run Parameters dialog.
- Run Stochastic Model – Opens the the Model Steering dialog to start the stochastic model run.
- GSSHA to HEC-RAS
HEC-RAS Model Control
When materials are mapped to cross sections a material ID is stored for the line segment properties. In order to properly link the material ID with a roughness when exporting the GIS file for HEC-RAS an Area Property coverage must be linked to a cross section database. The HEC-RAS Model Control dialog allows making this specification. If no definition has been provided when exporting the GIS file, a prompt will ask to make the association before proceeding with the export.
Hydraulic Model Boundary Conditions
The Hydraulic Model Boundary Conditions dialog allows assigning flow change locations and selecting hydrographs.
HEC-RAS Stochastic Modeling
WMS allows model linkages between HEC-1, HEC-RAS, and floodplain delineation for the purpose of performing the stochastic simulation. These simulations can be developed from either of the three modeling menus. Read more about the stochastic simulation in the Stochastic Modeling article.
Related Topics
- 1D Hydraulic Modeling
- Import and Export GIS Files
- Managing Cross Sections
- Bridges/Culverts
- Area Property Coverage
- Extracting Cross Sections
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||