WMS:SMPDBK: Difference between revisions
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
* [[WMS:Defining Roughness|Defining Roughness]] | * [[WMS:Defining Roughness|Defining Roughness]] | ||
* [[WMS:SMPDBK Post Processing|Post Processing]] | * [[WMS:SMPDBK Post Processing|Post Processing]] | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 22 March 2013
The Simplified Dam-Break (SMPDBK) was developed by the National Weather Service (NWS) for predicting downstream flooding produced by a dam failure. This program is still capable of producing the information necessary to estimate flooded areas resulting from dam-break floodwaters while substantially reducing the amount of time, data, and expertise required to run a simulation of the more sophisticated unsteady NWS DAMBRK, or now called FLDWAV. The SMPDBK method is useful for situations where reconnaissance level results are adequate, and when data and time available to prepare the simulation are sparse. Unlike the more sophisticated versions of DAMBRK and FLDWAV, the SMPDBK method does not account for backwater effects created by natural channel constrictions of those due to such obstacles as downstream dams or bridge embankments.
The input required for a SMPDBK model is a stream centerline, cross sections, and information regarding the storage and failure of the dam being modeled. WMS saves the model data to a properly formatted input file for SMPDBK and then launches the executable. The executable is the same version distributed by the NWS. When a model is successfully run, WMS will automatically read the results and create a water surface elevation data set that can be used for automated floodplain delineation as illustrated in the picture below.
Centerline
The centerline must be defined in a 1D-Hydraulic Centerline coverage and consists of a single feature arc that should start at the dam being modeled and end at or just after the last cross section. The centerline determines the extents of the simulation and helps to establish the stationing of cross sections that are defined along its length. You should create centerlines from the upstream (dam side) end to the downstream end in order to provide the proper direction to the model.
Cross Sections
Cross sections for a simplified dam-break analysis must be defined in a 1D-Hydraulic Cross Section coverage. A minimum of two cross sections are required (upstream and downstream ends of the river to be modeled), but sufficient cross sections to define the floodplain should be included. If you are using a digital terrain model to extract cross sections then it is fairly simple to include additional cross sections without the requirement of a field survey.
SMPDBK uses a table of top-widths corresponding to incremental elevations to define the cross sections. WMS will compute 8 incremental depths automatically for each cross section since this is the maximum number of increments allowed by SMPDBK. The eight increments are equal and determined based on the low and high elevations of the cross section. Manning's roughness values can be determined for segments of the cross section based on an area property coverage.
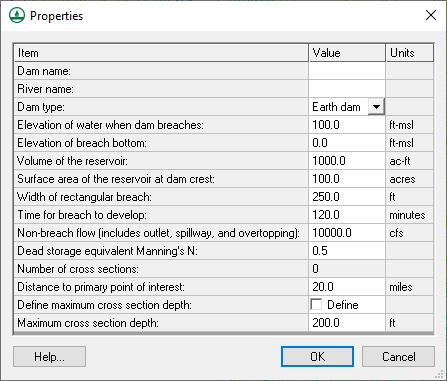
SMPDBK Dam Properties
The Dam Properties dialog (from Edit Parameters of the SMPDBK menu) is used to set several options which describe the dam. This dialog is pictured below.
Data for this dialog can be collected by searching for the data on the Internet. Data could also be obtained from the National Inventory of Dams web site at http://geo.usace.army.mil/pgis/f?p=397:1:0 (2004).
Running a Simulation
The SMPDBK executable is distributed with WMS and should be present in the WMS program directory (SMPDBK.EXE). When choosing the Run Simulation command you will be prompted for a file name that WMS will use to write the properly formatted input based on the centerline, cross section, roughness, and dam properties defined. After writing the input file WMS will launch the SMPDBK executable and pass the newly created input file as a command line argument.
Export Simulation
If you wish to save a completed SMPDBK input file that is properly formatted then you can choose the Export SMPDBK File command. You could then continue to edit/prepare the file in a text editing program such as Notepad or Wordpad and then run it through the SMPDBK program outside of WMS. However, an SMPDBK formatted input file is always generated when running a simulation from within WMS.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||